Comprehensive Approaches to COVID-19 Mortality Prediction: Insights from Studies in Reggio Emilia
SARS-CoV-2 disease (COVID-19) impacted the whole world during 2020, and the number of infected patients and mortality grew rapidly throughout 2021. Chest X-ray Radiography (CXR) were the standard diagnostic protocol for pneumonia due to its simplicity and speed. High-resolution computed tomography (HRCT) was used for deeper investigations.
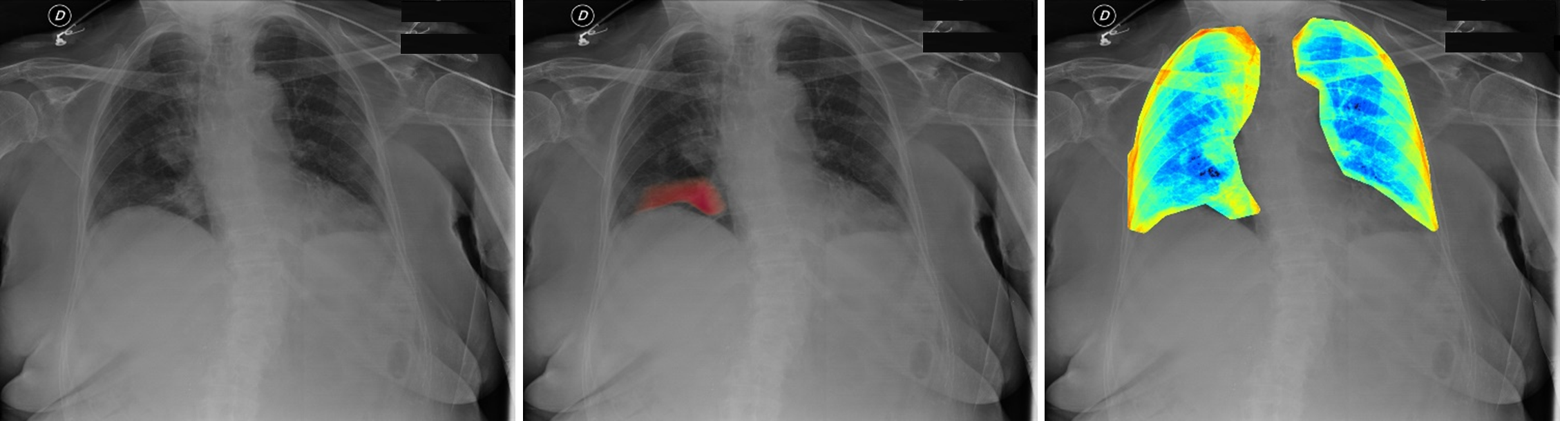
Two studies conducted in the Province of Reggio Emilia aimed to develop robust prognostic models for predicting COVID-19 mortality using different approaches. The first study focused on chest X-rays (CXRs), involving 1816 patients. Radiomic and neural network features were extracted, and machine learning models (AdaBoost, Quadratic Discriminant Analysis, and Random Forest) achieved robust mortality predictions.
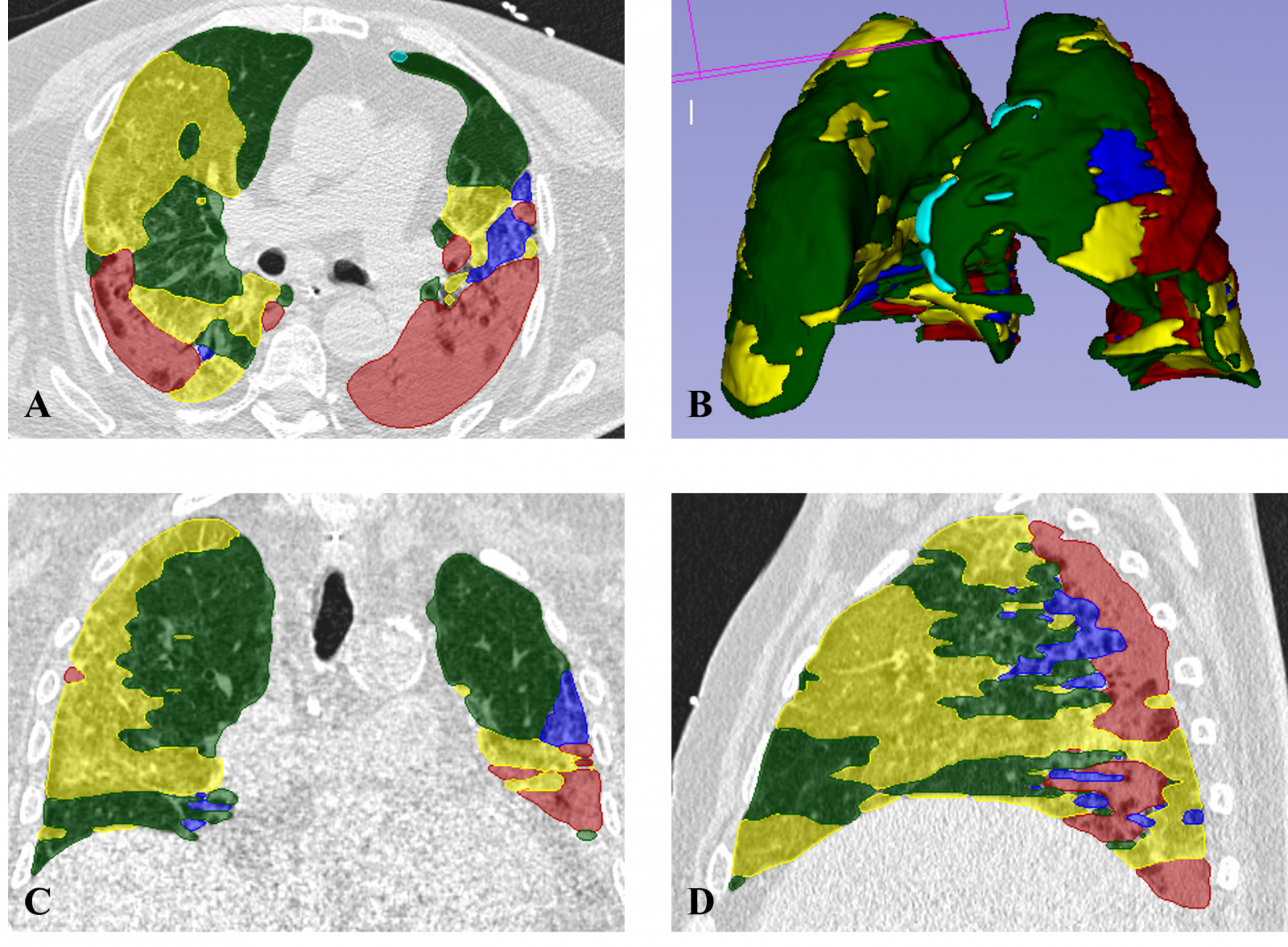
The second study enrolled 2348 patients and proposed a user-friendly tool for COVID-19 mortality prediction using both machine learning (support vector machine) and deep learning (feedforward neural network) approaches. Clinical and radiomic features were employed, and the best performance, with an AUC of 0.803 for machine learning and 0.864 for deep learning, was achieved by combining both sets of information.
The studies suggest the potential for these models in clinical practice beyond COVID-19 mortality prediction. Our pipeline represents an important tool for the early screening of COVID-19 patients to limit criticalities and to appropriately allocate the (limited) resources available. It could also address similar scenarios, helping clinicians to assess the severity of the disease and promptly stratify the patient population to support the decision of a personalized care pathway.
Ultimo aggiornamento: 27/02/25
